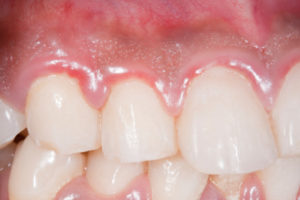
What is gum enlargement and how is it treated?
Gum enlargement or gingival hyperplasia can be painful and can affect your oral health. Gum enlargement is cause by overgrowth of the gum tissue. Several health issues can cause gum enlargement. Gum enlargement can be cause by three common problems 1.) gum inflammation, 2.) medication, and 3.) genetics.
- Gum inflammation induced enlargement
Gum inflammation is a common reason for the gums to become enlarged. Enlarged gum inflammation is likely cause by plaque or other infections. The enlargement may be localized to a specific area of the gum. When bacteria infect the gums, the body’s immune response will trigger an inflammatory response. The inflammatory response can cause the gums to feel tender, bleed easily and become red. Gum enlargement due to inflammation is usually attributed to poor hygiene that leads to infection or periodontal disease. Inflammation induced gum enlargement can be easily treated by practicing good oral hygiene. Removing the source that is causing inflammation can easily resolve gum enlargement.
- Medication induced gum enlargement
Another cause of gum enlargement is medication. Some medications have side effects that can cause the gums to enlarged. Typical features of gum enlargement induced by medications are gums that feel firm, looks pale pink, and gums that do not bleed as easily. In severe cases, gum enlargement induced by medications can completely cover the crown of the tooth. When gum overgrowth covers the surfaces of the tooth, this can make cleaning the teeth difficult. This can lead to periodontal disease and tooth decay. To treat gum enlargement due to medication is to stop taking the medication after consulting with a physician and dentist. Gum enlargement is reversible after stopping medication use. However, if the medication cannot be discontinued, the enlarged gums can be surgically removed to prevent overgrowth.
- Genetics induced gum enlargement
A third cause of gum enlargement is genetics. Some people who inherits a rare genetic disorder call gingival fibromatosis may start to develop enlarged gums early in childhood. This form of gum enlargement can be difficult to treat since it is an inherited disease. If left untreated the gums can completely cover the teeth. In children, this can lead to dental caries and teeth alignment issues. To prevent gum enlargement, surgery is necessary to remove the excess growth to prevent tooth impaction and tooth displacement. Continue surgical treatment may be required because the overgrowth cannot be stop.
What are the surgical methods used to treat gum overgrowth?
Treating gum overgrowth often depends on the root cause of the overgrowth. The simplest treatment is just by practicing good oral hygiene. However, if the cause of overgrowth cannot be treated with good oral hygiene, surgery may be necessary. Some procedures used to treat overgrown gums can include periodontal surgery, gingivectomy, lasers, or electrosurgery. In such cases, a periodontist can perform the surgery to remove excess gum overgrowth.
Gum enlargement can lead to severe oral health issues if left untreated. If you have questions or concerns about the health of your gums, call California Dental Group at (800) 407-0161 to schedule your next appointment.